Introduction:
Designing a product is like embarking on a journey. And every journey begins with a prototype—a preliminary version of your product that helps you test, iterate, and refine your ideas. But when it comes to prototypes, not all are created equal. In the world of design, there are two main types: low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. Each serves a unique purpose and offers distinct advantages. So, let’s dive in and explore the differences between low-fidelity and high-fidelity design prototypes.
What Are Prototypes?
Before we delve into the specifics of low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes, let’s take a step back and understand what prototypes are. Prototypes are early-stage models or representations of a product, typically created to test and validate design concepts. They allow designers to explore ideas, gather feedback, and make informed decisions before moving forward with development.
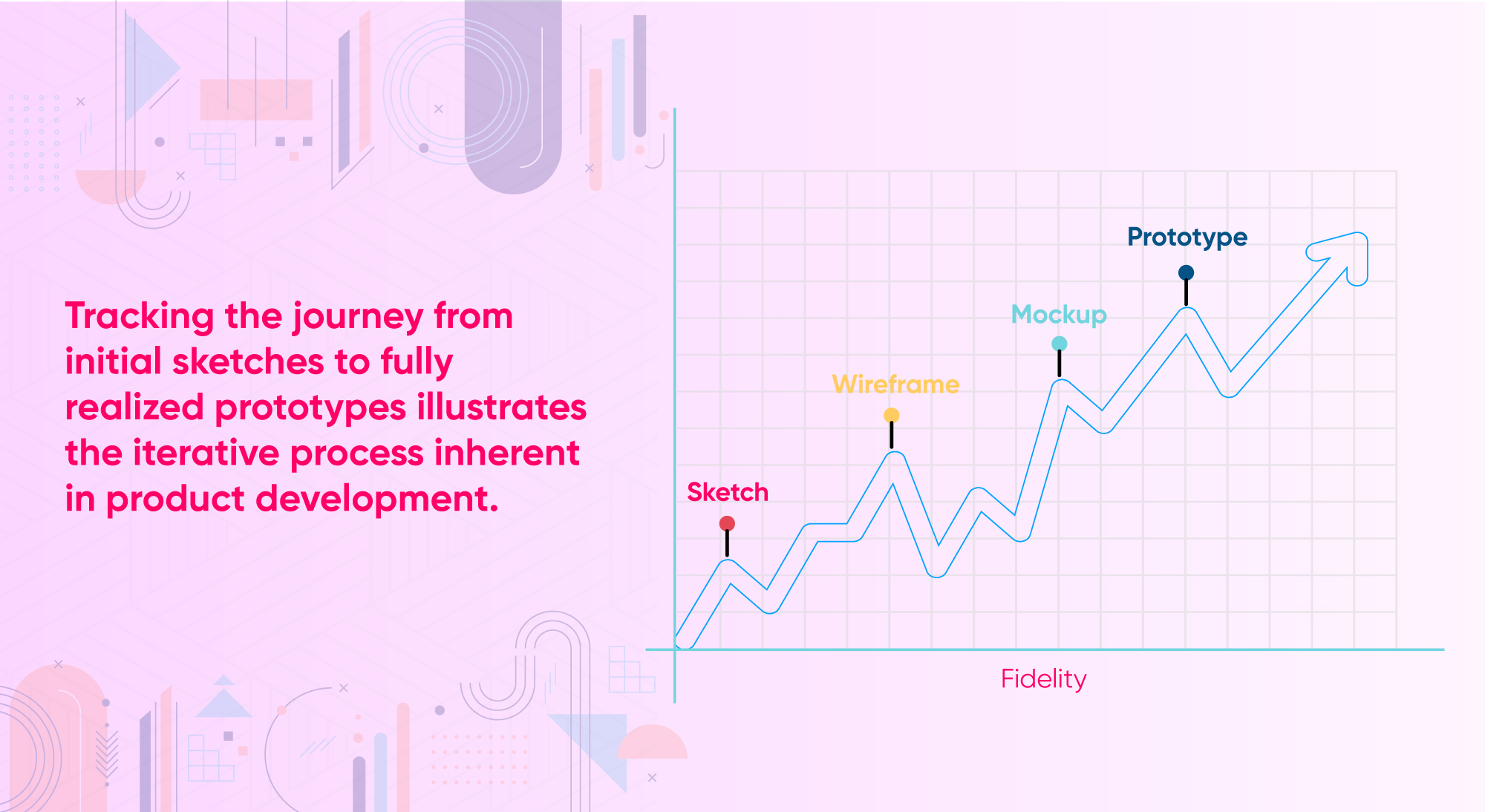
Fidelity is about making sure a prototype acts and behaves like the final product in UX design.?
Fidelity in UX design refers to the level of detail and realism in a prototype or design. It encompasses how closely the prototype represents the final product in terms of visual appearance, functionality, and interactivity. Fidelity can vary along a spectrum, ranging from low to high fidelity.
- Low-fidelity (low-fi) prototypes are simple, basic representations of the product, often created quickly and with minimal detail. They focus on conveying the core concepts and functionality without getting bogged down by visual polish.
- High-fidelity (high-fi) prototypes, on the other hand, are more detailed and closely resemble the final product. They incorporate realistic visuals, interactive elements, and advanced functionality to provide a more accurate representation of the user experience.
Fidelity in UX design is crucial because it influences how users perceive and interact with the prototype. Low-fidelity prototypes are often used in the early stages of design to explore ideas and gather feedback, while high-fidelity prototypes are used later in the process for user testing and validation. The level of fidelity chosen depends on the goals of the design process and the stage of development.
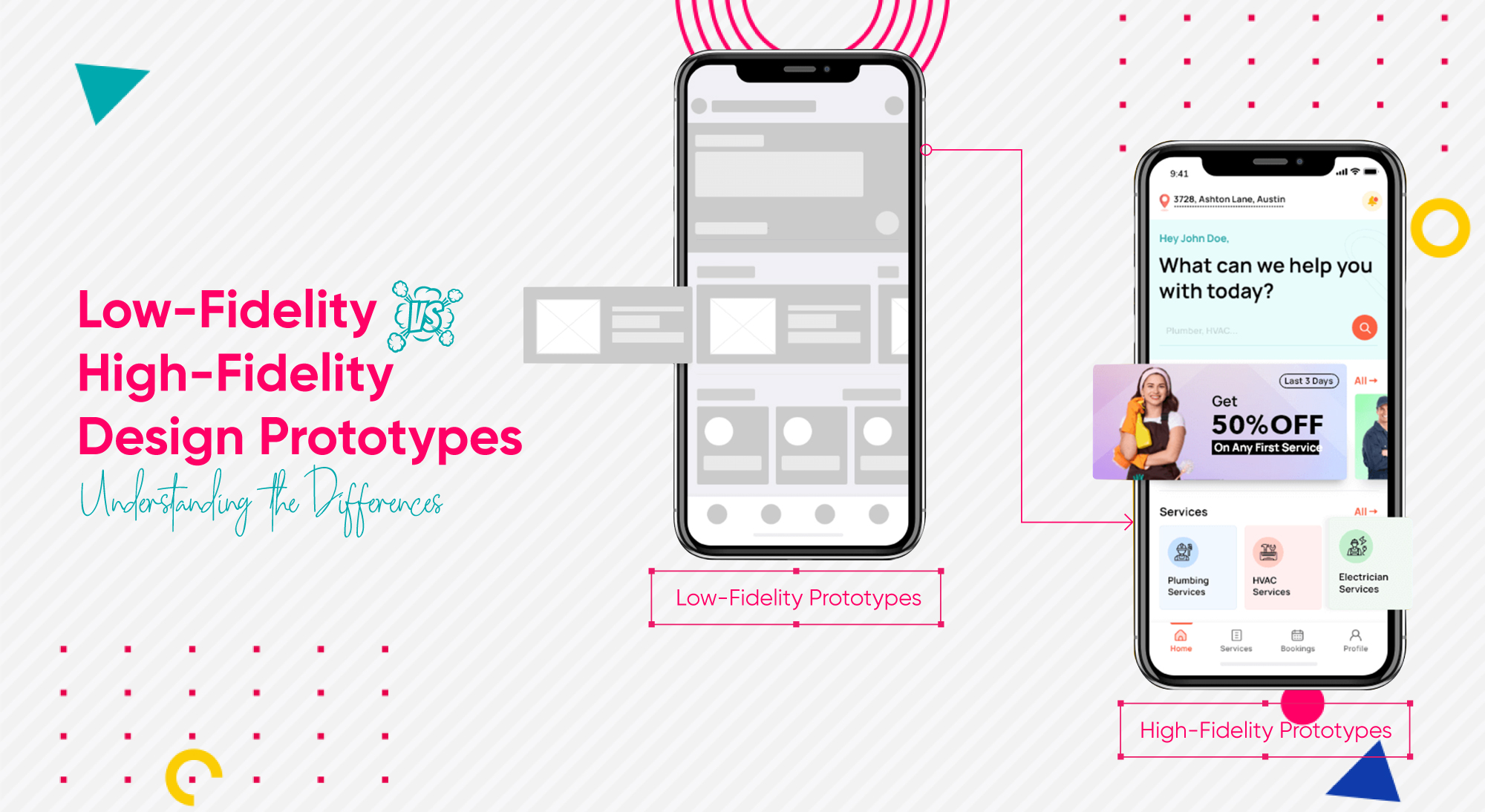
Low-Fidelity Design Prototypes:
Low-fidelity prototypes, often abbreviated as low-fi, are simple, rough, and quick to create. They are usually the first iteration of a design concept and serve as a visual sketch or blueprint of the product. Here’s what you need to know about low-fidelity design prototypes:
- Basic and Simplified: Low-fi prototypes focus on conveying the core functionality and structure of the product without getting bogged down by details.
- Minimalistic Design: They are characterized by minimal visual polish, using basic shapes, placeholders, and rough sketches to represent elements.
- Quick and Inexpensive: One of the key advantages of low-fi prototypes is their speed and cost-effectiveness. They can be created using pen and paper or digital tools in a matter of minutes.
- Ideal for Concept Exploration: Low-fidelity prototypes are perfect for brainstorming sessions and exploring multiple design ideas quickly.
High-Fidelity Design Prototypes:
On the other end of the spectrum, we have high-fidelity prototypes, also known as high-fi. These prototypes are more polished, detailed, and closely resemble the final product. Here’s what sets high-fidelity design prototypes apart:
- Realistic and Detailed: High-fi prototypes aim to simulate the look, feel, and interactions of the final product as closely as possible. They incorporate realistic visuals, animations, and interactive elements.
- Close to Final Product: These prototypes closely mimic the user interface and user experience of the final product, providing a more accurate representation of how the product will look and behave.
- Comprehensive Testing: High-fidelity prototypes are well-suited for user testing and validation, as they offer a more immersive and realistic experience for users to interact with.
- Time-Intensive: Unlike low-fi prototypes, high-fi prototypes require more time and resources to create due to their detailed nature and advanced functionality.
Choosing Between Low-Fidelity and High-Fidelity Prototypes:
Now that we’ve explored the characteristics of both low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes, you might be wondering which one to use for your project. Here are some factors to consider when making that decision:
- Project Stage: In the early stages of a project when you’re still exploring concepts and gathering feedback, low-fidelity prototypes are ideal. They allow for rapid iteration and experimentation without investing too much time or resources.
- Complexity of Interactions: If your product involves complex interactions or relies heavily on visual details, high-fidelity prototypes may be more suitable. They provide a more realistic representation of the final product and allow for comprehensive testing of user interactions.
- Budget and Timeline: Consider your budget and timeline constraints when choosing between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. Low-fi prototypes are more cost-effective and quicker to produce, making them a practical choice for projects with limited resources or tight deadlines.
- User Testing Goals: Think about your goals for user testing. If you’re primarily focused on validating basic functionality and gathering early feedback, low-fidelity prototypes may suffice. However, if you need to test more advanced features or assess the overall user experience, high-fidelity prototypes offer a more realistic testing environment.
Top Prototyping Tool Recommendations:
Figma:
Figma is a powerful design and prototyping tool that allows real-time collaboration between team members. It offers a wide range of features for designing and prototyping web and mobile interfaces.
Adobe XD (Experience Design):
Adobe XD is a popular choice among designers for creating interactive prototypes. It offers a seamless workflow with other Adobe Creative Cloud apps and provides features for wireframing, designing, and prototyping.
Sketch:
Sketch is widely used for designing user interfaces and creating interactive prototypes. It offers an extensive library of plugins and integrations that enhance its functionality for prototyping.
InVision:
InVision is a comprehensive prototyping tool that allows designers to create interactive prototypes and collaborate with stakeholders. It offers features for creating animations, transitions, and user flows.
Axure RP:
Axure RP is a robust prototyping tool that is commonly used for creating complex interactive prototypes, particularly for web and desktop applications. It offers features for creating dynamic content and simulating user interactions.
Proto.io:
Proto.io is a web-based prototyping tool that is known for its ease of use and powerful features. It offers a drag-and-drop interface for creating prototypes and supports animations, gestures, and transitions.
Marvel:
Marvel is a simple yet powerful prototyping tool that is suitable for both designers and non-designers. It offers features for creating interactive prototypes and user flows, as well as collaboration and feedback tools.
Origami Studio:
Origami Studio, developed by Facebook, is a prototyping tool that is tailored for creating interactive prototypes for mobile apps. It offers a visual interface for designing and prototyping user interfaces, animations, and gestures.
Principle:
Principle is a prototyping tool specifically designed for creating animations and interactive prototypes for mobile apps. It offers a timeline-based interface for designing and previewing animations.
ProtoPie:
ProtoPie is a prototyping tool that focuses on creating interactive prototypes for mobile apps and smart devices. It offers a unique interaction model that allows designers to create complex interactions without coding.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic world of design, prototyping is an essential tool for bringing ideas to life and refining them into successful products. Whether you opt for low-fidelity or high-fidelity prototypes depends on various factors such as project stage, complexity, budget, and testing goals. By understanding the differences between low-fidelity and high-fidelity design prototypes, you can make informed decisions and create prototypes that effectively communicate your vision and engage your audience. So, embrace the prototyping process, experiment with different approaches, and let your creativity soar!





2 Comments
XMC.PL
Reading this felt like finding a long-lost treasure — a piece of writing that enlightens and comforts in equal measure.
xmc.pl
Your writing unfolds with delicate rhythm, where phrases harmonize to form a reflective cadence. Each sentence encourages attentive reading, lingering contemplation, and a meditative awareness of layered meaning.